Schedule a Presentation With Us!
- PapaCarie for Caries Removal
- PerioMonitor Saliva Test
- Woodpecker Laser Smart Blue
- Woodpecker Endodontic

We use cookies!
We use cookies to improve your website experience and analyze traffic. These cookies are necessary for the site to function properly and help us understand how you use it. The information collected remains anonymous and is used for analysis purposes only. By continuing to browse our site, you accept the use of these cookies. If you do not want your data to be used in this way, please click decline. You can read our document on the potection of personal information (Law 25) here

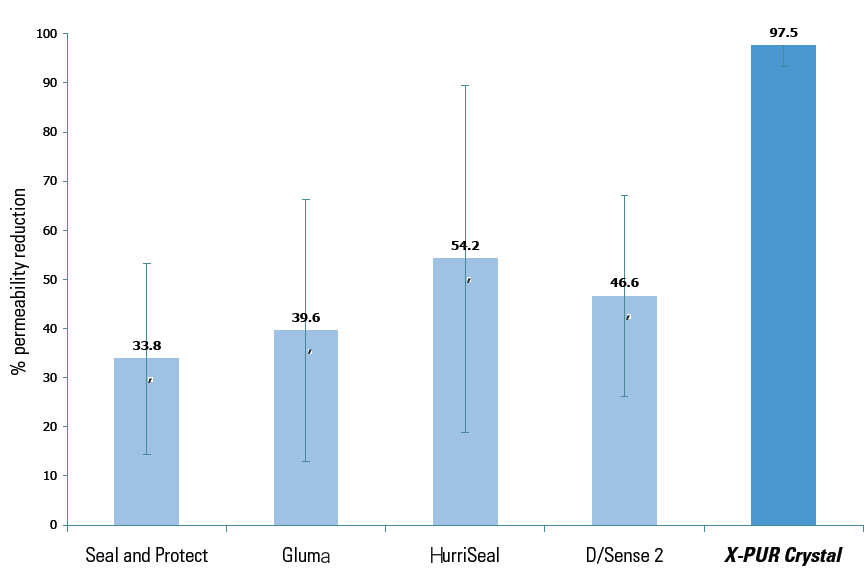
X-PUR Crystal is a water-based potassium oxalate in-office desensitizer made of natural acids and salts that quickly form insoluble calcium crystals. It provides effective patient relief for the general root, or exposed dentin sensitivity, in only a few seconds. This innovative blend rapidly blocks the fluid flow to help provide relief from sensitivity. It is uniquely different than other desensitizers on the market because it does not have to be refrigerated. For extra patient comfort, it can be warmed to body temperature or slightly above. X-PUR Crystal is efficient, cost-effective and safe.
Enamel, dentin and cementum are composed of high concentrations of alkaline calcium hydroxyapatite (HAp). X-PUR Crystal reacts with HAp to rapidly form millions of acid resistant chelate precipitates within the dentinal tubules at depths of 7-12 μm and on the surfaces of the vital dentin substrate, this action creates a long-lasting seal, preventing patient hypersensitivity and blocking bacteria penetration to the vital pulp.
Proprietary blend of natural acids and salts
Do not etch X-PUR Crystal’s low pH formulation. It dissolves immediately, does not harm soft-tissues, and effectively removes the smear layer.
Adults
Directions for Use Under a Restoration or Crown

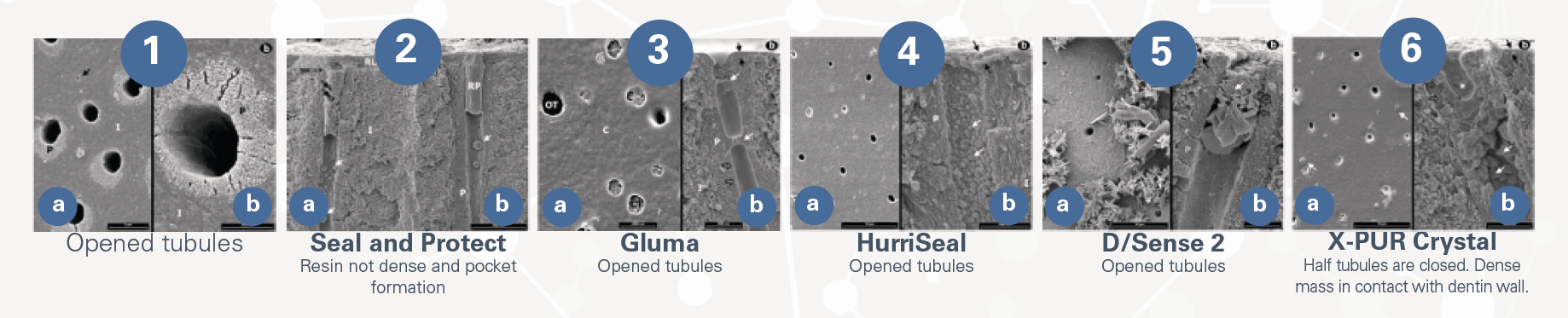
* Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) image of the very dense peritubular dentin (calcium hydroxyapatite) and the very small crystals along the inner wall which are insoluble calcium crystals that assist to relieve patient discomfort.
Any appearance of a frosty-white surface indicates the blockage of the dentin tubules. May be applied to a damp surface and dabbed around crown margins and onto the exposed tooth roots that are sensitive to cold or air stimuli. No light curing is necessary.